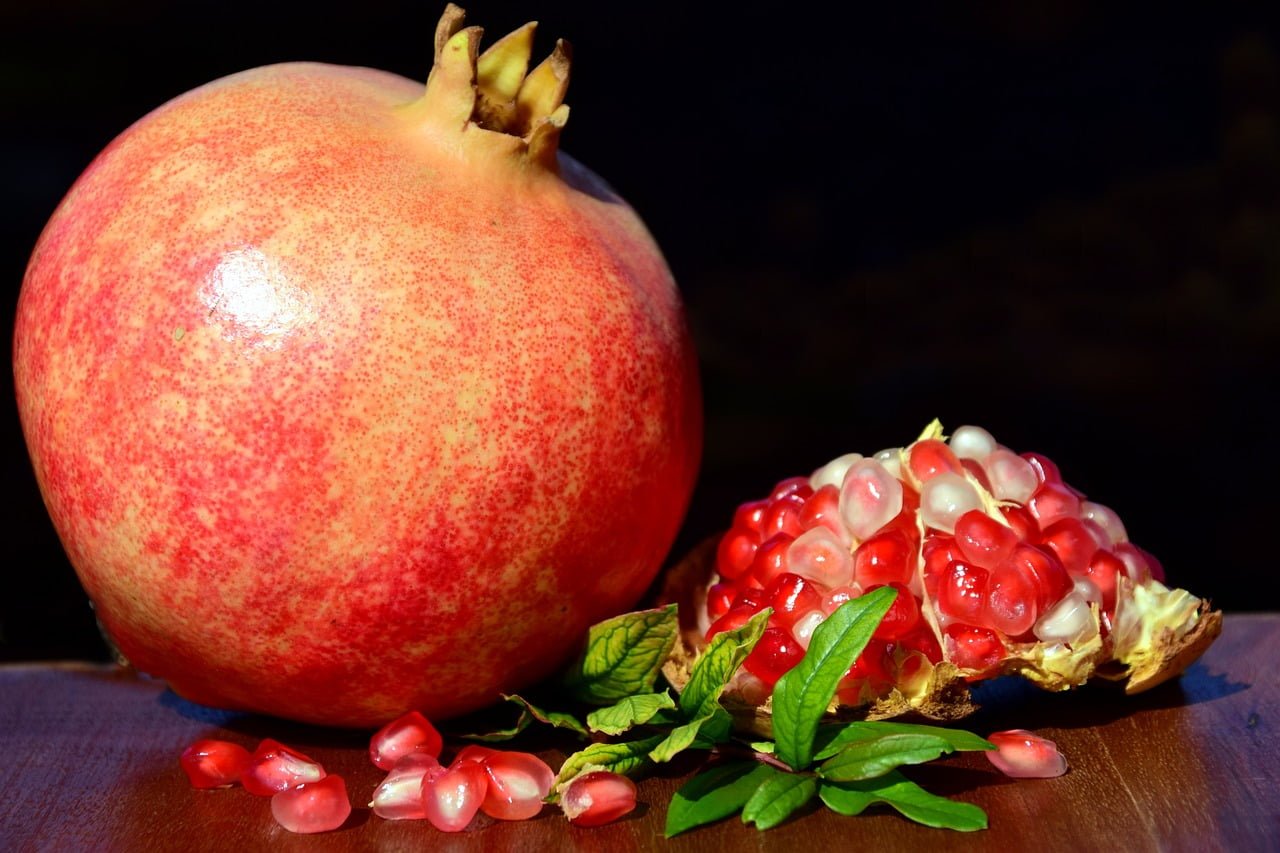
Can we eat pomegranate seeds?
Yes, you can absolutely eat pomegranate seeds! Those jewel-like arils (the official name for the juicy seed coverings) are not only safe but also pack a nutritional punch. Let’s explore why you should enjoy these tasty seeds and how to easily incorporate them into your meals.
Why Pomegranate Seeds Are a Superfood
- Nutrient Powerhouses: Pomegranate seeds are loaded with vitamins (especially vitamin C and K), minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients work together to boost your overall health.
- Antioxidant Rich: The antioxidants in pomegranate seeds help fight inflammation and protect your cells from damage. This may lower your risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and certain cancers.
- Heart Health Hero: Studies suggest that pomegranate seeds may help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and promote healthy blood flow – all good news for your heart.
- Gut-Friendly Fiber: The fiber in pomegranate seeds keeps your digestive system running smoothly, preventing constipation and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
How to Enjoy Pomegranate Seeds
- Eat Them Straight: The simplest way is to enjoy them fresh, right out of the pomegranate. Their sweet-tart flavor is a delicious snack on its own.
- Sprinkle on Salads: Add a burst of color and flavor to your salads with pomegranate seeds. They pair well with leafy greens, feta cheese, and nuts.
- Blend into Smoothies: Toss a handful into your morning smoothie for an extra dose of nutrients and a beautiful hue.
- Top Your Yogurt: Pomegranate seeds make a vibrant and nutritious topping for yogurt, oatmeal, or chia pudding.
Creative Ways to Use Pomegranate Seeds
- Garnish for Dishes: Sprinkle pomegranate seeds over roasted vegetables, grilled meats, or even desserts for an elegant touch.
- Add to Salsa or Guacamole: The sweet-tart flavor adds a unique twist to your favorite dips.
- Make Pomegranate Molasses: Reduce pomegranate juice to create a tangy, sweet-tart syrup to drizzle over desserts, meats, or even cocktails.
Important Considerations
- Allergies: While rare, some people can be allergic to pomegranates. If you experience any symptoms like itching or swelling after eating them, seek medical advice.
- Medication Interactions: If you’re taking any medications, especially blood thinners, consult
This article is reviewed by Russel, before publishing. If you have any doubt, you can contact us or consult with your nearby doctor. Remember, in medical matters, there is no same advice, cure, and medicine for all.