Can we eat apple seeds?
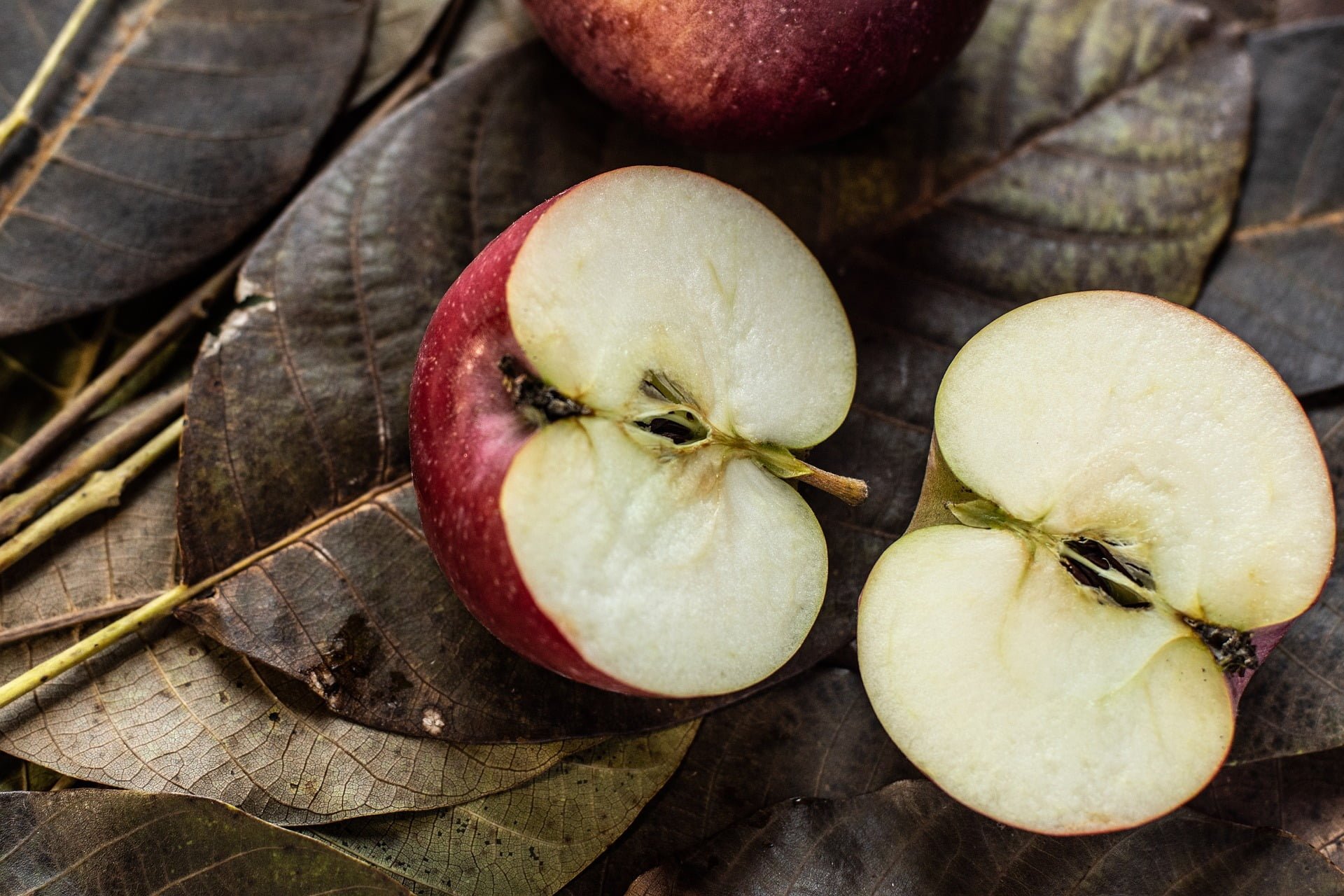
Apple seeds, like those in many other fruits, contain compounds that have raised questions about their safety for human consumption. One of the main concerns is the presence of a compound called amygdalin, which can release cyanide when metabolized. This has led to the popular belief that consuming apple seeds can be harmful. However, the reality is a bit more nuanced.
Composition of Apple Seeds:
Apple seeds contain a small amount of amygdalin, a natural substance found in many stone fruits and seeds. When amygdalin comes into contact with digestive enzymes, it can release cyanide. Cyanide is a toxic substance that, in large enough quantities, can be harmful or even fatal to humans.
The Amount Matters:
The key factor to consider when determining whether apple seeds are safe to eat is the quantity. Apple seeds contain very low levels of amygdalin. To reach a toxic dose of cyanide from apple seeds alone, one would need to consume a massive quantity – far beyond what you’d typically ingest when eating apples.
Casual Consumption Is Safe:
In normal, everyday consumption of apples, including the seeds, there is no need to worry about cyanide poisoning. Chewing and swallowing a few apple seeds from time to time while eating an apple is unlikely to cause any harm. Your body can safely metabolize the small amounts of cyanide released.
Health Benefits of Apple Seeds
When it comes to the health benefits of apple seeds, it’s important to approach this topic with caution. While apple seeds do contain certain compounds that may offer potential health advantages, they are also associated with risks due to the presence of cyanide-producing amygdalin.
While apple seeds do contain certain nutrients and compounds that may have theoretical health benefits, these benefits are typically associated with minimal quantities that have a negligible impact on overall nutrition. The potential risks posed by the release of cyanide when consuming large amounts of apple seeds far outweigh any possible benefits. As such, it’s advisable to approach apple seeds with caution and prioritize their safe consumption as part of whole apples, rather than as a dietary supplement. If you have specific health concerns or dietary questions, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.

Myths and Misconceptions
Apple seeds have been the subject of various myths and misconceptions, often leading to confusion about their safety and potential health effects. Let’s debunk some common myths and clarify the facts surrounding apple seeds:
Myth: Apple Seeds Are Highly Toxic:
- Fact: While apple seeds do contain compounds that can release cyanide when metabolized, the amount of cyanide is exceptionally low. In typical consumption of whole apples, including the seeds, there is no need to worry about cyanide poisoning.
Myth: A Few Apple Seeds Can Be Lethal:
- Fact: It’s extremely unlikely that consuming a few apple seeds will lead to cyanide poisoning. The human body can safely metabolize small amounts of cyanide.
Myth: Chewing Apple Seeds Is Dangerous:
- Fact: While crushing or chewing apple seeds can release slightly more amygdalin (the compound that can produce cyanide), the levels are still minuscule and not a cause for concern during normal apple consumption.
Myth: Apple Seeds Should Always Be Avoided:
- Fact: For most adults, consuming apple seeds as part of eating whole apples is generally safe. However, it’s essential to do so in moderation and not deliberately ingest large quantities of seeds.
Myth: Apple Seeds Cure Cancer:
- Fact: Claims that apple seeds or the compounds they contain can cure cancer are not supported by scientific evidence. Such claims are misleading and potentially dangerous.
Apple Seeds in Culinary Uses
While apple seeds are typically disregarded or even avoided due to concerns about their cyanide content, they can add intriguing dimensions to culinary creations when used thoughtfully and in moderation. The nutty, slightly bitter flavor and pleasing crunch of apple seeds can enhance various dishes:
In baking and cooking, ground apple seeds can serve as a unique ingredient, adding texture and a subtle nutty undertone to bread, muffins, cookies, sauces, stuffing, and savory dishes like roasted meats and fish. Crushed apple seeds also make a delightful nutritional garnish for salads, cereals, yogurt, and desserts, offering both flavor and a satisfying crunch.
For those inclined toward DIY snacks, roasted and seasoned apple seeds can elevate homemade trail mixes or snack blends, providing an unexpected twist. Their distinct texture and mild nutty taste make them a worthy inclusion.
Infusing apple seed oil or vinegar with crushed seeds can impart a subtle apple essence to dressings, marinades, and drizzles. Likewise, steeping crushed apple seeds in hot water or adding them to teas and infusions creates beverages with a hint of apple flavor.
In culinary experimentation, some adventurous chefs explore the creative potential of apple seeds, incorporating them into innovative dishes or using them as alternative spices in place of traditional options like nutmeg or cinnamon.
Eating Apple Seeds Safely
Enjoying apple seeds safely requires a balanced approach that considers both their potential risks and the culinary possibilities they offer. Here’s a guide to safely incorporate apple seeds into your diet:
1. Moderation is Key: The most critical aspect of safe apple seed consumption is moderation. In everyday eating, including the seeds of a few apples is generally safe for adults. However, deliberately ingesting large quantities of apple seeds is not recommended, as it could lead to the release of higher levels of cyanide, albeit still unlikely to be harmful.
2. Avoid Deliberate Ingestion: While casual consumption of apple seeds as part of eating whole apples poses no significant danger, deliberately ingesting large amounts of apple seeds should be avoided. The tiny amounts of cyanide released during metabolism can accumulate to potentially harmful levels when consumed excessively.
3. Mindful Chewing: If you choose to chew apple seeds, be mindful that crushing or chewing them can release slightly more amygdalin, the compound that produces cyanide. However, the levels remain minuscule and typically pose no risk during regular apple consumption.
4. Seed-Free for Young Children and Pets: It’s advisable to avoid giving apple seeds to young children or pets. Their smaller bodies may be more susceptible to the effects of cyanide, even in small amounts. Ensure that apples served to children or pets are seed-free.
5. Diversify Your Diet: While apple seeds can be a part of your diet, it’s essential to maintain a diverse and balanced diet, incorporating a wide range of fruits, vegetables, and foods to meet your nutritional needs.
6. Consult a Healthcare Professional: If you have specific health concerns or dietary restrictions, consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance. They can provide tailored advice based on your individual circumstances.
Growing Apple Trees from Seeds
Growing apple trees from seeds can be a rewarding and educational experience, but it’s important to understand that the resulting trees may not necessarily produce apples of the same quality as their parent tree. Here’s a brief guide to get you started:
1. Collecting Seeds: Begin by collecting apple seeds from ripe, healthy apples. Clean the seeds by removing any fruit residue and allowing them to air dry.
2. Cold Stratification: Apple seeds require a period of cold stratification to break their dormancy and prepare for germination. Place the cleaned seeds in a damp paper towel or a bag with moistened peat moss, and refrigerate them for about 6-8 weeks.
3. Germination: After the cold stratification period, sow the seeds in pots filled with potting soil. Water them regularly and ensure they receive adequate sunlight. Germination may take several weeks, and not all seeds may sprout.
4. Transplanting: Once the seedlings have grown large enough, transplant them to larger containers or outdoors in a well-prepared garden bed. Choose a sunny location with well-draining soil.
5. Vigilant Care: Young apple trees require careful nurturing. Regular watering, protection from pests, and pruning to encourage strong growth are essential.
6. Patience is Key: It’s important to note that apple trees grown from seeds can take several years to mature and produce fruit. Furthermore, the fruit they produce may not resemble the apples from which the seeds were collected; they may even be less desirable in terms of taste and quality.
7. Grafting: To ensure that the resulting tree bears fruit of a specific variety, many orchardists choose to graft branches from a known apple tree onto the young seedling’s rootstock. This technique allows for the preservation of desired apple characteristics.
While growing apple trees from seeds can be a fascinating project, it’s essential to be patient and realistic about the results. Apple trees produced from seeds often exhibit genetic variability and may not yield apples identical to the parent tree. For consistent and high-quality fruit production, grafting is typically the preferred method among orchardists and experienced gardeners.
Conclusion
In summary, casual consumption of apple seeds within the context of eating apples is generally safe for adults. The small amount of amygdalin in apple seeds is unlikely to cause harm when ingested in typical quantities. However, as with many aspects of nutrition, moderation is key. Deliberate ingestion of large amounts of apple seeds is not recommended. If you have concerns or specific dietary restrictions, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance.
This article is reviewed by Russel, before publishing. If you have any doubt, you can contact us or consult with your nearby doctor. Remember, in medical matters, there is no same advice, cure, and medicine for all.