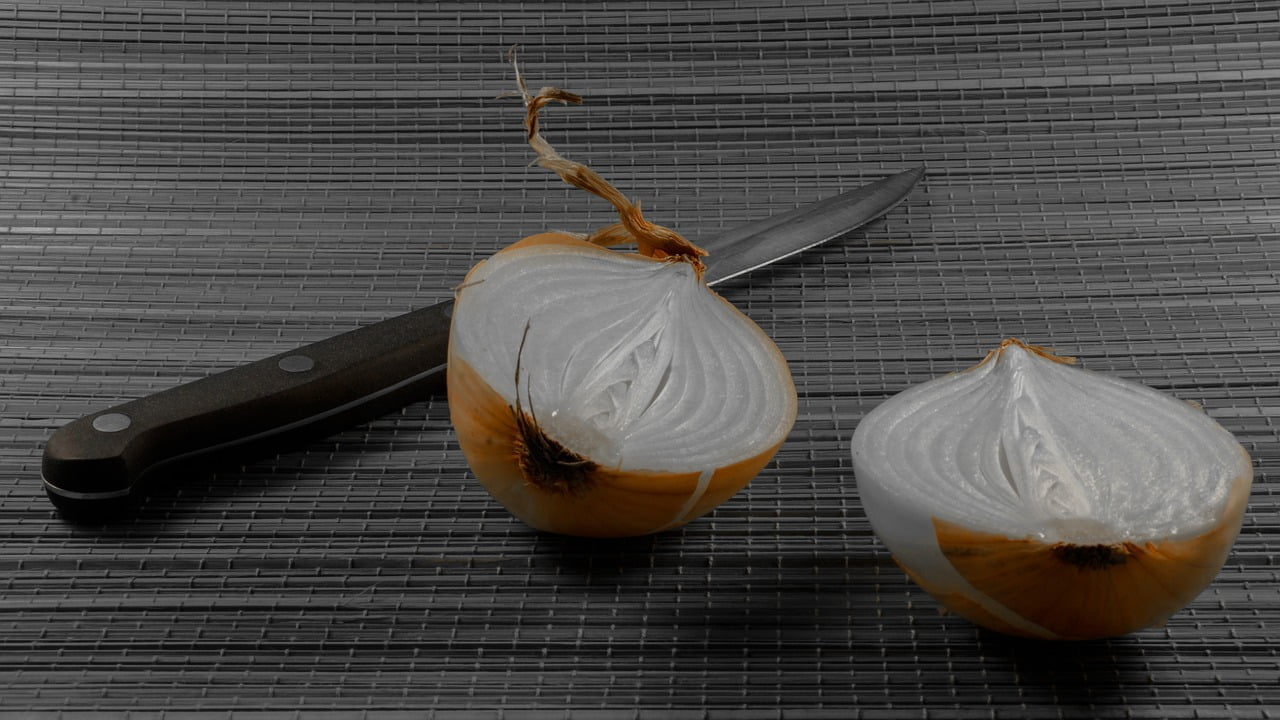
Can We Eat Onion Skins?
Can We Eat Onion Skins? Yes, you can eat onion skins, but they are not commonly consumed in their whole form. Onion skins are technically edible, but they are usually tough and papery, making them less appealing for direct consumption. Instead, they are typically removed and discarded before cooking or eating onions.
However, onion skins are not without value. They contain certain nutrients and antioxidants, including dietary fiber and quercetin, which can provide health benefits. If you want to incorporate onion skins into your diet, it’s advisable to do so in a way that makes them more palatable. One approach is to finely chop or blend them to make them easier to consume or to use them as a seasoning or flavoring agent in soups, broths, and stews. Cooking onion skins can help soften their texture and release their mild onion flavor.
The Surprising Benefits of Consuming Onion Skins
Consuming onion skins may not be a common practice, but they offer several surprising benefits when used thoughtfully in your diet. Here are some of the potential advantages of incorporating onion skins into your meals:
- Nutrient-Rich: Onion skins contain various nutrients, including dietary fiber, quercetin (a powerful antioxidant), and other phytochemicals. These compounds contribute to overall health and may help combat oxidative stress in the body.
- Waste Reduction: Utilizing onion skins reduces food waste, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to cooking. Instead of discarding the skins, you can put them to good use.
- Flavor Enhancement: Onion skins provide a mild onion flavor, making them an excellent natural seasoning for soups, broths, and stews. They add depth and complexity to dishes without the need for additional artificial flavorings or seasonings.
- Cost-Effective: Using onion skins as a flavoring agent can save you money since you’re making the most of the entire onion, minimizing waste, and reducing the need for other flavor enhancers.
- Antioxidant Properties: Quercetin, found in onion skins, has been associated with various health benefits, including reducing inflammation and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
- Digestive Health: The dietary fiber in onion skins can support digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation.
- Immune Support: Some studies suggest that quercetin may have immune-boosting properties, helping your body defend against infections.
- Skin Health: Antioxidants like quercetin can also benefit your skin by protecting it from free radicals that can lead to premature aging.
- Reducing Allergies: Quercetin may have antihistamine properties, which can help alleviate allergy symptoms for some individuals.
While these potential benefits are intriguing, it’s essential to remember that onion skins are not typically consumed in large quantities. They are best used as a flavoring agent or seasoning rather than as a primary food source. Additionally, if you decide to include onion skins in your diet, ensure they are thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants. Overall, while consuming onion skins may not be a dietary staple, they can be a valuable
Are Onion Skins Safe to Eat? A Closer Look
Taking a closer look at the safety of eating onion skins is important, as they are not commonly consumed in their whole form. Here are some key considerations regarding the safety of consuming onion skins:
- Edibility: Onion skins are technically edible, and they are not considered toxic. However, they are typically removed and discarded before cooking or eating onions due to their tough and papery texture.
- Cleaning: If you intend to eat onion skins, it’s crucial to clean them thoroughly. Like the outer layers of most vegetables, onion skins can come into contact with dirt, pesticides, or contaminants during cultivation and transportation. Washing them well before use helps minimize the risk of consuming any potential contaminants.
- Texture: The primary reason people avoid eating onion skins is their texture. They are tough, fibrous, and can be unpleasant to chew when consumed in their whole form. To make them more palatable, you can finely chop or blend them, or use them as a seasoning or flavoring agent in soups and stews.
- Nutritional Value: Onion skins do contain some nutrients and antioxidants, such as dietary fiber and quercetin. These compounds have potential health benefits, but you can often obtain them from other parts of the onion and a more varied diet.
- Allergies: While onion skins themselves are not a common allergen, some individuals may be sensitive to certain components in onions. It’s essential to be aware of any personal allergies or sensitivities when considering the consumption of onion skins.
- Cooking: Cooking onion skins can help soften their texture and release their mild onion flavor. They are often used as a natural flavoring agent in broths and soups, enhancing the taste of the dish.
Creative Ways to Incorporate Onion Skins into Your Diet
Incorporating onion skins into your diet can be a creative and sustainable way to minimize food waste while adding a subtle onion flavor to your dishes. Here are some imaginative ways to use onion skins:
- Broths and Soups: Perhaps the most common use for onion skins is in making flavorful broths and soups. Simply add thoroughly cleaned onion skins to your stockpot along with other vegetables and seasonings. They infuse the liquid with a mild onion essence, enhancing the overall taste of your soups.
- Infused Vinegar or Oil: Make your own flavored vinegar or oil by placing onion skins in a clean, dry container and covering them with vinegar or oil. Over time, the skins will impart their subtle onion flavor to the liquid. Use this infused vinegar or oil in salad dressings, marinades, or as a finishing touch to your dishes.
- Homemade Seasoning Powder: Dry and grind onion skins into a fine powder to create a unique seasoning blend. This powder can be sprinkled on roasted vegetables, popcorn, or any dish in need of a savory kick.
- Tea or Infusions: Surprisingly, you can use onion skins to brew a mild, earthy tea or infusion. Steep cleaned onion skins in hot water for a soothing drink. You can also blend them with other herbs and spices for a more complex flavor profile.
- Gravies and Sauces: Add a handful of onion skins to your homemade gravies and sauces. They contribute depth of flavor and color, enriching your culinary creations.
- Pickling: Enhance your pickling brine with the subtle onion notes of onion skins. They work well with pickled vegetables, adding a delicate onion essence to the tangy brine.
- Flavorful Rice: When cooking rice, toss a few onion skins into the pot for an aromatic twist. They’ll infuse the rice with a subtle onion aroma, elevating your side dish.
- Natural Food Coloring: Onion skins can be used as a natural food coloring agent. Simmer them in water, strain the liquid, and use it to color rice, dough, or even Easter eggs.
- Cocktail Garnish: For a unique cocktail garnish, dry onion skins and twist them into decorative shapes. They can add a visually intriguing element to your drinks while subtly infusing them with a hint of onion flavor.

Nutritional Value of Onion Skins
Onion skins, although not typically consumed in large quantities, do contain some nutritional value, including various nutrients and antioxidants. Here’s a closer look at the nutritional components found in onion skins:
- Dietary Fiber: Onion skins contain dietary fiber, which is beneficial for digestive health. Fiber aids in regular bowel movements, helps prevent constipation, and may contribute to a feeling of fullness, assisting in weight management.
- Quercetin: Quercetin is a flavonoid antioxidant found in onion skins, known for its potential health benefits. It has anti-inflammatory properties and may help protect cells from oxidative stress. Some studies suggest that quercetin may support heart health and reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases.
- Phytochemicals: Onion skins contain various phytochemicals, which are natural compounds found in plants. These phytochemicals can have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potentially protective effects on overall health.
- Minerals: Onion skins contain trace amounts of essential minerals like calcium, potassium, and magnesium. While the levels are relatively low, they still contribute to your daily mineral intake.
- Vitamins: Onion skins contain small amounts of vitamins, primarily vitamin C. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that supports the immune system and helps the body absorb iron from plant-based foods.
Historical and Cultural Perspectives on Eating Onion Skins
Historical and cultural perspectives on eating onion skins vary widely across different regions and time periods. In some cultures, onion skins have been utilized for their potential health benefits and culinary uses, while in others, they have been overlooked as a food source.
Historically, onion skins have been associated with traditional medicine practices in various parts of the world. In some cultures, they were used in herbal remedies and folk medicine due to their perceived health-promoting properties, such as their antioxidant content. Additionally, onion skins were sometimes employed as a natural dye for textiles, imparting a range of earthy colors.
Culinary traditions have also incorporated onion skins in creative ways. Some cuisines use onion skins to infuse soups and broths with a subtle onion flavor, adding depth to their dishes. They have also been employed as a seasoning or garnish in certain recipes.
However, it’s important to note that the consumption of onion skins has not been universally embraced. In many cultures, the outer layers of onions have been routinely discarded due to their tough texture and perceived lack of palatability. Instead, the focus has traditionally been on the edible flesh and bulbs of the onion.
Sustainability and Reducing Food Waste
Sustainability and reducing food waste have become increasingly important topics in recent years, as they have significant environmental, economic, and social implications. Here’s an overview of the importance of sustainability and strategies to reduce food waste:
Importance of Sustainability:
- Environmental Impact: Food production has a substantial environmental footprint. It requires land, water, energy, and other resources. When food is wasted, it contributes to unnecessary resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Costs: Food waste represents a significant economic burden. Consumers, businesses, and governments spend money on producing, transporting, and disposing of food that is never consumed. Reducing food waste can lead to cost savings at all levels of the supply chain.
- Food Security: As the global population continues to grow, ensuring food security for all becomes increasingly challenging. Reducing food waste can help address this issue by making more food available for consumption.
Strategies to Reduce Food Waste:
- Meal Planning: Plan meals in advance, create shopping lists, and buy only what you need. This reduces the chances of buying excess food that might go to waste.
- Proper Storage: Store food correctly to extend its shelf life. This includes using airtight containers, keeping perishables in the refrigerator, and freezing items that won’t be used soon.
- Understanding Date Labels: Understand date labels (such as “use by” and “best before”) to avoid prematurely discarding food that is still safe to eat. These labels are often misunderstood, leading to unnecessary waste.
- Portion Control: Serve and eat appropriate portions to minimize leftovers. Consider using smaller plates and containers to help with portion control.
- Creative Cooking: Get creative with leftovers and use them in new dishes. Leftover vegetables, for example, can be used in soups, stir-fries, or omelets.
Sustainability and reducing food waste require a collective effort involving individuals, businesses, governments, and organizations. By adopting these strategies and promoting a culture of responsible consumption, we can make significant progress toward a more sustainable and food-secure future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sustainability and the reduction of food waste are vital components of responsible consumption that have far-reaching impacts on our environment, economy, and society. Recognizing the importance of these issues, individuals, businesses, and governments around the world are taking proactive steps to address them.
By implementing strategies such as meal planning, proper storage, portion control, and creative cooking, individuals can contribute to reducing food waste in their daily lives. Additionally, understanding date labels and supporting food donation initiatives can make a significant difference.
Businesses and industries play a crucial role in minimizing food waste throughout the supply chain, from production and distribution to retail and consumer consumption. Innovative technologies and data-driven solutions are helping companies track and reduce waste, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits.
Government policies and regulations can further incentivize food waste reduction efforts. These policies may include tax incentives, food labeling standards, and waste diversion programs. Supporting such policies can accelerate progress in curbing food waste on a larger scale.
Education and awareness initiatives are also essential in changing attitudes and behaviors toward food waste. By fostering a culture of responsible consumption, we can collectively reduce waste, conserve resources, and enhance food security.
In a world where hunger persists alongside food waste, and environmental sustainability is a pressing concern, addressing food waste is not only an ethical imperative but also a practical necessity. By embracing sustainable practices and working collaboratively, we can move toward a future where food is valued, resources are conserved, and all communities have access to nutritious meals.
Related Posts
This article is reviewed by Russel, before publishing. If you have any doubt, you can contact us or consult with your nearby doctor. Remember, in medical matters, there is no same advice, cure, and medicine for all.